Abstract
Introduction
This phase 1/2 study evaluated the safety and antitumor activity of brentuximab vedotin (BV) administered in combination with nivolumab (Nivo) in adult patients (pts) with relapsed/refractory classic Hodgkin lymphoma (R/R cHL) who have failed frontline therapy (NCT02572167). Results from Parts 1 & 2 have been previously reported, wherein safety, efficacy, and biomarkers consistent with immune activation were observed in pts with R/R cHL (Herrera et al., Blood 2018). In Part 3, patients were treated with BV + Nivo on Day 1 of each cycle. In contrast, pts in Parts 1 & 2 received BV on C1D1 and Nivo on C1D8 with concurrent admin on subsequent cycles. Herein we present safety, efficacy, and biomarker results for Part 3 and updated progression free survival (PFS) from Parts 1 & 2.
Methods
Pts in Parts 1 & 2 received up to four 21-day cycles of staggered dosing (day 1 BV 1.8 mg/kg, day 8 Nivo 3 mg/kg in Cycle 1) and concurrent thereafter, with steroid and antihistamine premedication. Pts in Part 3 received up to four 21-day cycles of concurrent BV + Nivo on Day 1 with antihistamine premedication. Following Cycle 4 response assessment (Lugano Classification Revised Staging System with the incorporation of the Lymphoma Response to Immunomodulatory Therapy Criteria [LYRIC, 2016]) responding pts were eligible to undergo autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT).
Results
30 pts were treated in Part 3 and all were evaluable for efficacy. Pt characteristics included the following: median age 31.5 yrs (range; 20 - 66), 63% female, 93% prior ABVD, 37% primary refractory HL, 30% relapsed within 1year of frontline therapy, 30% with extranodal disease and 17% with bulky disease at enrollment. 28 pts completed all 4 cycles. 1 pt discontinued treatment (tx) due to an adverse event (AE; Grade 3 [G3] elevated Gamma-Glutamyltransferase) and 1 pt due to progressive disease (PD). The latter pt eventually died due to PD. All pts are off tx and have been observed through the safety reporting period.
37% of pts experienced a G3 or higher tx emergent AE prior to ASCT. 30% of the pts experienced infusion related reactions (IRRs), which occurred most frequently during Cycle 2. Potential G3 or higher immune-related AEs (IRAEs), excluding IRRs, occurred in 2 pts, one of whom required steroids for G4 pneumonitis, which subsequently resolved.
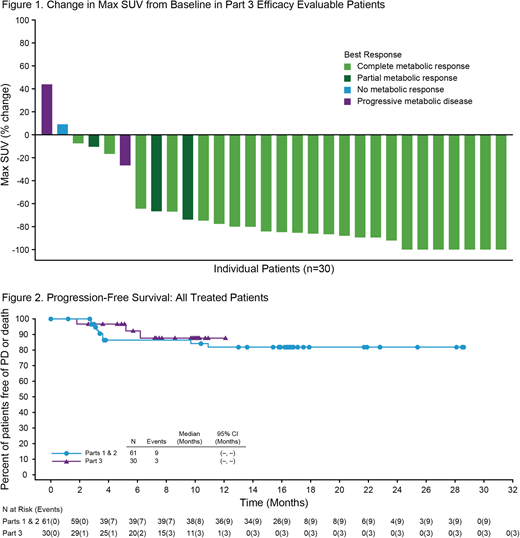
Among the 30 efficacy evaluable pts, the complete response (CR) rate was 80% (24/30), with an objective response rate (ORR) of 93%. 47% of pts (14) had a Deauville ≤2, and 17% (5) had Deauville 3. 5 pts with CR had a Deauville >3 and met LYRIC criteria for IR-2. 4/5 pts had a negative follow-up biopsy that confirmed CR and in 1 pt the PET finding was considered to be a false positive as contrast enhanced CT did not reveal any abnormality. All 5 pts proceeded directly to ASCT and remain in CR at follow-up. Among all treated patients, 25 went directly to ASCT after completing BV + Nivo tx with a median 6.8 x 106 CD34+ cells/kg (range 1-20) collected. Median times to neutrophil and platelet engraftment were 12 and 14 days, respectively. 4 pts required additional salvage therapy subsequent to study tx. Patients were followed for a median of 6 months from ASCT (N=25, range 0.8-8.8) and 10 months from first dose (N=30, range 1.8-12.7). The estimated 9-month PFS rate in all-treated pts was 88%. This is comparable to all-treated pts in Parts 1 & 2, whose estimated 9 and 15 month PFS were 86% and 82%, respectively (Fig 2).
Biomarker testing was performed on peripheral blood samples, included immunophenotyping, serum cytokine analysis, and TCRβ sequencing. Concurrent dosing of BV+ Nivo resulted in increased levels of both activated and dividing CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, as well as increased regulatory T-cells and circulating plasmablasts. Cytokines and chemokines associated with innate and adaptive immune activation, including Type I and Type II interferons, IL-18, and IP-10, were significantly upregulated following BV + Nivo, while TARC levels were significantly diminished following therapy. TCRβ sequencing revealed clonal expansion in the periphery following BV + Nivo.
Conclusion
A concurrent dosing schedule of BV + Nivo was well tolerated with a high CR rate of 80%. Biomarkers evaluated in Part 3 indicate immune activation in the periphery following BV + Nivo. Cumulatively, the results in Part 3, along with the durable remissions noted in Parts 1 & 2, support BV + Nivo combination as an encouraging first salvage therapy prior to ASCT in pts with R/R cHL.
Advani:Forty Seven: Research Funding; Infinity: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board, Research Funding; Gilead/Kite: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board; Roche/Genentech: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board, Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Agensys: Research Funding; Millenium: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Autolus: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kura: Research Funding; Kyowa: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board; Bayer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board; Regeneron: Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board; Cell Medica: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board; Pharmacyclics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Participated in an advisory board, Research Funding. Moskowitz:Bristol Myers-Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria; Merck: Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Bartlett:Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; KITE: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Vose:Celgene: Research Funding; Legend Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.: Research Funding; Incyte Corp.: Research Funding; Roche: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Research Funding; Acerta Pharma: Research Funding; Abbvie: Honoraria; Epizyme: Honoraria; Kite Pharma: Research Funding. Ramchandren:Merck: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics LLC an AbbVie Company: Consultancy, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding. Feldman:Johnson and Johnson: Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Speakers Bureau; Pharmacyclics: Speakers Bureau; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Portola: Research Funding; Janssen: Speakers Bureau; KITE: Speakers Bureau. LaCasce:Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Honoraria; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Other: Data safety and monitoring board; Research to Practice: Speakers Bureau; Humanigen: Consultancy, Honoraria. Christian:Acerta: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Immunomedics: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Genentech: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Ansell:LAM Therapeutics: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Regeneron: Research Funding; Merck & Co: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Celldex: Research Funding; Trillium: Research Funding; Affimed: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding. Moskowitz:Celgene: Consultancy; Merck & Co: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Research Funding. Fenton:Seattle Genetics, Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Ogden:Seattle Genetics, Inc: Employment, Equity Ownership. Taft:Seattle Genetics: Employment, Equity Ownership. Zak:Seattle Genetics: Employment, Equity Ownership. Sacchi:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Employment, Equity Ownership. Galderisi:Seattle Genetics: Employment, Equity Ownership. Herrera:Immune Design: Research Funding; Merck, Inc.: Consultancy, Research Funding; KiTE Pharma: Consultancy, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Gilead Sciences: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal